Looking for students or interns
Areas of expertise
Information optics , Photoacoustic microscopy , Ultra-fast and biophotonic imaging
- Full Professor
- Scientific head of the Laboratory of Applied Computational Imaging
- Holder of Canada Research Chair in Ultrafast Computational Imaging
Phone
514-228-6812
E-mail
jinyang.liang@inrs.ca
Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre
1650 Lionel-Boulet Blvd.
Varennes, Quebec J3X 1P7
Canada
Research interests
Our research focuses on laser modulation techniques in novel optical imaging devices. Currently, we are working on the following three areas:
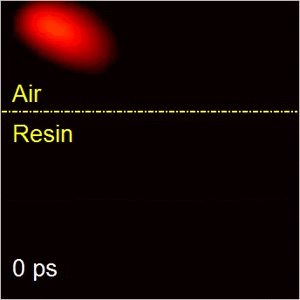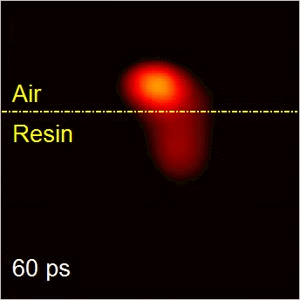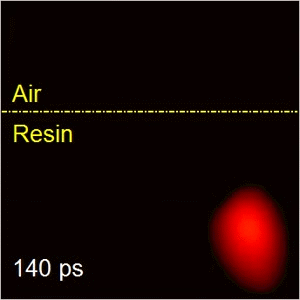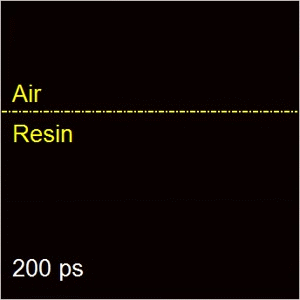
Compressed ultrafast photography (CUP)
CUP is the world’s fastest receive-only camera. Synergistically combining compressed sensing and streak imaging, CUP can image transient events at 100 billion frames per second with a single camera exposure. CUP’s operating principle consists of hardware-based image acquisition and software-based image reconstruction. CUP has led to many high-profile publications, including Nature (selected as the cover story) and Science Advances. CUP has also produced two patents licensed to Axis Photonics.
Our group is further advancing CUP technology from both technological development and novel applications. CUP for physics and biomedicine applications. We are also working with Axis Photonics to commercialize this technique.

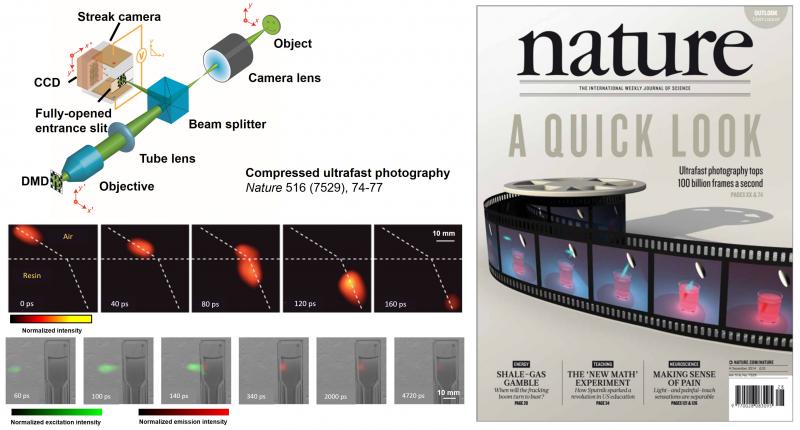
Selected publications:
- Nature 516, 74-77 (2014).
- Science Advances 3, e1601814 (2017).
- Optica 5, 1113-1127 (2018).Light: Science and Application 7, 42 (2018).
- Optics Letters 44, 1387-1390 (2019).
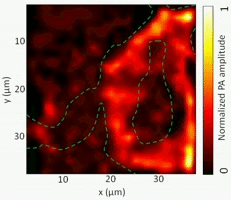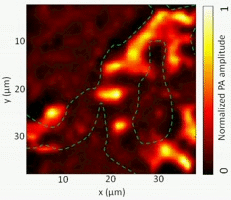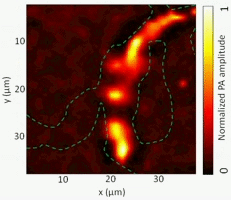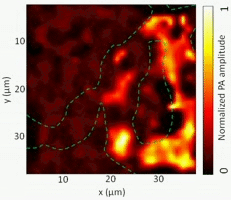
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT)
PAT has emerged as an attractive technique for label-free imaging in deep biological tissue. The present invention relates to a method for the production of heat-shrinkable particles. We are also collaborating with biologists and physicists in Montreal to explore novel applications of PAT.

Selected publications:
- Optics Letters 39, 430-433 (2014).
- Journal of Biomedical Optics 18, 096004 (2013).
High-precision laser beam shaping
Precisely shaping the laser beam to desired profiles is of great significance in physics. We have developed a high-precision laser beam shaper, which can shape an incident laser pulse into arbitrary patterns with unprecedented intensity accuracy. This technique has been adopted by many research groups in a condensed matter for the generation of programmable optical potentials. It has contributed recent breakthrough in Bose-Einstein condensation.
We are continuing exploring novel applications of this technique in laser physics, condensed matter physics, and metrology.

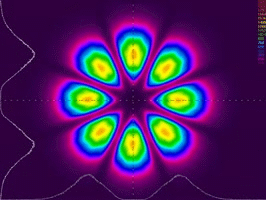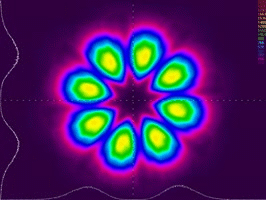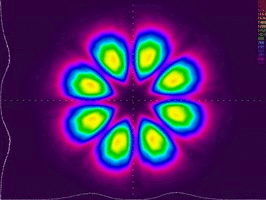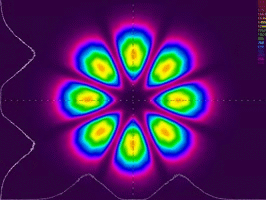
Selected publications :
- Applied Optics 49,1323-1330 (2010).
- Optical Engineering 51, 108201 (2012).Optics Express 21, 32013 (2013).
- Optics Letters 45, 964-967 (2020).