- Research
Discovery by François Légaré’s team could lead to more effective use of radiation therapy in oncology.

From left to right: Steve MacLean (CTO at Infinite Potential Laboratories), Sylvain Fourmaux (Research Associate at INRS), François Fillion-Gourdeau (Research Associate at Infinite Potential Laboratories), Stéphane Payeur (Research Officer at INRS), Simon Vallières (Postdoctoral Researcher at INRS) and François Légaré (Director EMT Centre).
Ultrafast laser technology continues to surprise. While research in this field may seem rather abstract at first glance, it very often leads to concrete applications. This is particularly true in healthcare, where the technology can be used to treat certain cancers.
This application was discovered by the research team at the Advanced Laser Light Source Laboratory (ALLS) of the Institut national de recherche scientifique (INRS), following recent work directed by the Professor and Director of the Énergie Matériaux Télécommunications Research Centre (EMT Centre), François Légaré. This work is the result of a collaboration with medical physicists at the McGill University Health Centre (MUHC). The study, published in the journal Laser & Photonics Reviews, presents astonishing results that call into question certain aspects of our knowledge about high-power laser pulses—knowledge that had become common in the scientific community.
“For the first time, we showed that, under certain conditions, a laser beam tightly focused in ambient air can accelerate electrons reaching energies in the MeV (megaelectronvolts) range, the same order of magnitude as some irradiators used in radiation therapy for cancer.”
François Légaré, Director of the EMT Centre, INRS
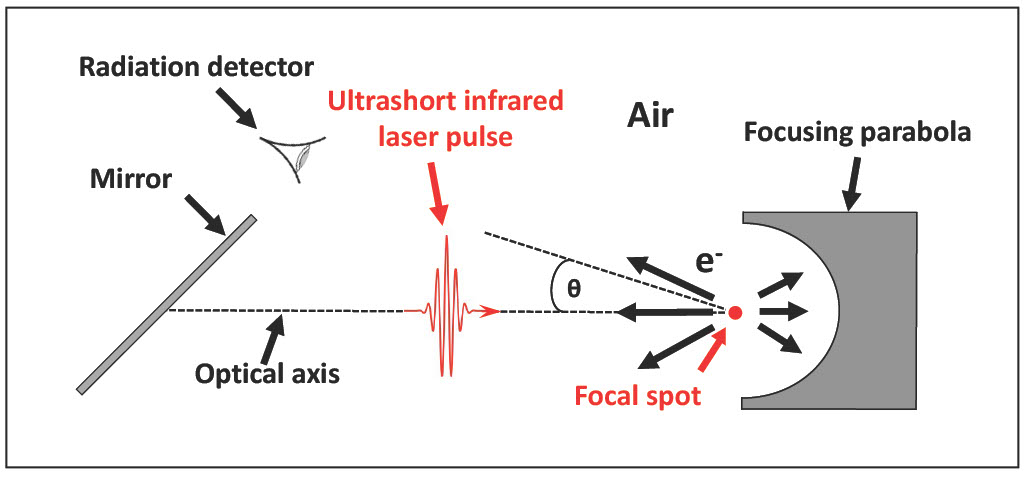
It was well established that focusing a laser pulse of sufficiently high intensity in ambient air would generate plasma at the focal point. This plasma acts as a source of electrons that can be accelerated to energies up to a few keV (kiloelectronvolts), at most. Until recently, it was not possible to reach higher energies in ambient air, due to a physical limitation.
The research team was able to demonstrate that electrons accelerated in ambient air can reach energies in the MeV (megaelectronvolts) range, i.e. around 1000 times greater than this previously insurmountable limit.
Better cancer treatment
The breakthrough achieved by the team at INRS’s EMT Centre opens the door to major advances in medical physics. A prime example is FLASH radiotherapy, a new approach to treating tumours that are resistant to conventional radiation therapy. It’s a technique that can be used to deliver high doses of radiation in an extremely short time ( microseconds rather than minutes). This better protects the healthy tissue around the tumour. This FLASH effect is still poorly understood in research but seems to involve a rapid deoxygenation of healthy tissues, reducing their sensitivity to radiation.
“No study has been able to explain the nature of the FLASH effect. However, the electron sources used in FLASH radiotherapy have similar characteristics to the one we produced by focusing our laser strongly in ambient air. Once the radiation source is better controlled, further research will allow us to investigate what causes the FLASH effect and to, ultimately, offer better radiation treatments to cancer patients.”
Simon Vallières, postdoctoral researcher and first author of the study
Safer handling
This discovery has concrete implications. Firstly, it requires extra caution when handling laser beams that are tightly focused in ambient air.
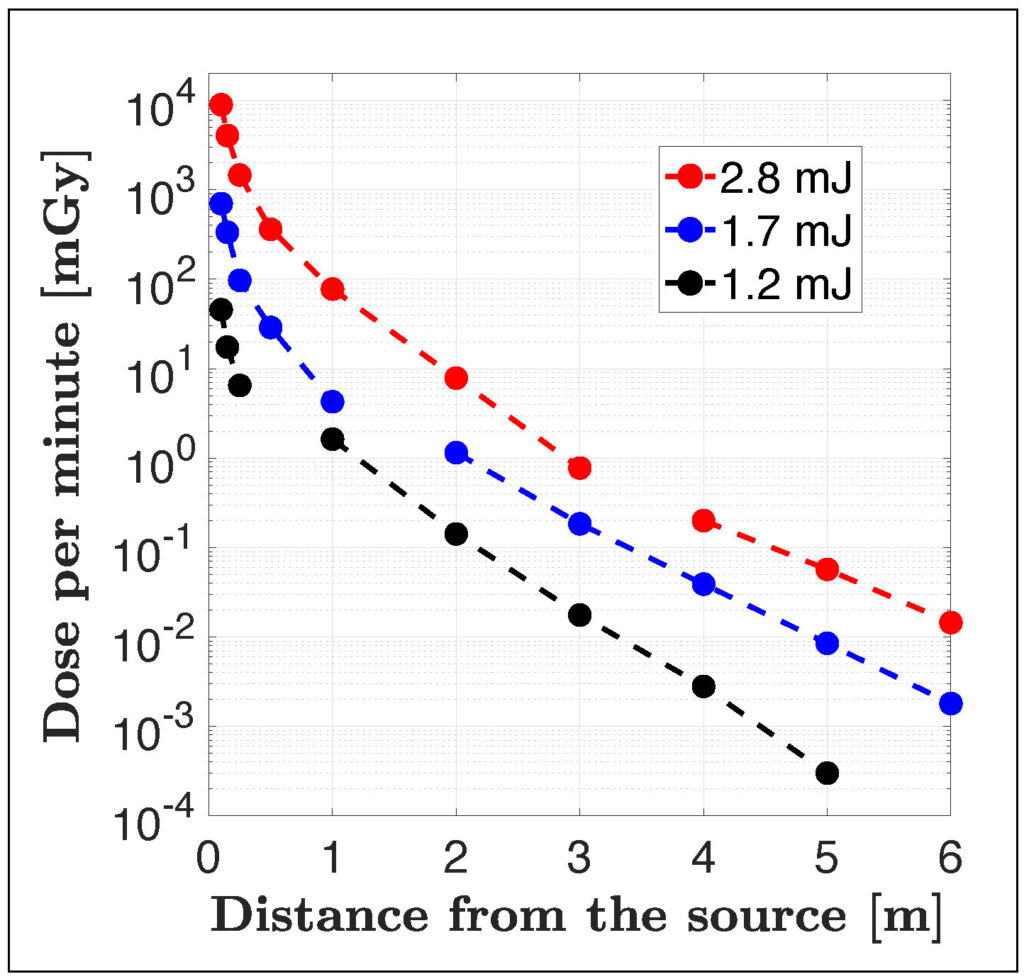
“The electron energies observed (MeV) allow them to travel more than three metres in air, or several millimetres under the skin. This poses a radiation exposure risk for users of the laser source,” explains Simon Vallières.
Moreover, by taking measurements near the source, the team observed a high radiation dose rate of electrons—three to four times greater than those used in conventional radiation therapy.
“Uncovering this radiation hazard is an opportunity to implement safer practices in laboratories,” says Simon Vallières. The young researcher notes that handling highly focused laser beams in ambient air must be done carefully, and that scientists need to avoid exposure to high doses of radiation as they are harmful to your health.
About ALLS
The Advanced Laser Light Source Laboratory (ALLS) is the only facility of its kind in Canada—a world-class research centre focused on developing a new type of laser with revolutionary applications. A member of the LaserNetUS network, the ALLS infrastructure has received funding from the Ministère de l’Économie, de l’Innovation et de l’Énergie (MEIE), and the Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) under the Major Scientific Initiative program.
About the paper
S. Vallières, J. Powell, T. Connell, M. Evans, M. Lytova, F. Fillion-Gourdeau, S. Fourmaux, S. Payeur, P. Lassonde, S. MacLean, F. Légaré. High Dose-Rate MeV Electron Beam from a Tightly-Focused Femtosecond IR Laser in Ambient Air. Laser Photonics Rev. 2023, 2300078. https://doi.org/10.1002/lpor.202300078
This research was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the Fonds de recherche du Québec – Nature and Technologies (FRQNT), and the Digital Research Alliance of Canada.